How to Install Nagios Server Monitoring on Ubuntu 16.04
Nagios is an open source software for system and network monitoring.
Nagios can monitor the activity of a host and its services, and provides
a warning/alert if something bad happens on the server. Nagios can run
on Linux operating systems. At this time, I'm using Ubuntu 16.04 for the
installation.
Prerequisites
- 2 Ubuntu 16.04 - 64bit servers
- 1 - Nagios Host with IP: 192.168.1.9
- 2 - Ubuntu Client with IP: 192.168.1.10
- Root/Sudo access
What we will do in this tutorial:
- Software the package dependencies like - LAMP etc.
- User and group configuration.
- Installing Nagios.
- Configuring Apache.
- Testing the Nagios Server.
- Adding a Host to Monitor.
Installing the prerequisites
Nagios requires the gcc compiler and build-essentials for the compilation, LAMP (Apache, PHP, MySQL) for the Nagios web interface and Sendmail to send alerts from the server. To install all those packages, run this command (it's just 1 line):
sudo apt-get install wget build-essential apache2 php
apache2-mod-php7.0 php-gd libgd-dev sendmail unzip
User and group configuration
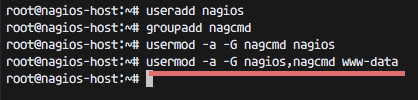
For Nagios to run, you have to create a new user for Nagios. We will name the user "nagios" and additionally create a group named "nagcmd". We add the new user to the group as shown below:useradd nagiosgroupadd nagcmdusermod -a -G nagcmd nagiosusermod -a -G nagios,nagcmd www-data
Installing Nagios
Step 1 - Download and extract the Nagios core
cd ~wget https://assets.nagios.com/downloads/nagioscore/releases/nagios-4.2.0.tar.gztar -xzf nagios*.tar.gzcd nagios-4.2.0
Step 2 - Compile Nagios
Before you build Nagios, you will have to configure it with the user and the group you have created earlier.
./configure --with-nagios-group=nagios --with-command-group=nagcmd
For more information please use: ./configure --help .Now to install Nagios:
make allsudo make installsudo make install-commandmodesudo make install-initsudo make install-config/usr/bin/install -c -m 644 sample-config/httpd.conf /etc/apache2/sites-available/nagios.confAnd copy evenhandler directory to the nagios directory:
cp -R contrib/eventhandlers/ /usr/local/nagios/libexec/chown -R nagios:nagios /usr/local/nagios/libexec/eventhandlers
Step 3 - Install the Nagios Plugins
Download and extract the Nagios plugins:
cd ~wget https://nagios-plugins.org/download/nagios-plugins-2.1.2.tar.gztar -xzf nagios-plugins*.tar.gzcd nagios-plugin-2.1.2/
Install the Nagios plugin's with the commands below:
./configure --with-nagios-user=nagios --with-nagios-group=nagios --with-opensslmakemake install
Step 4 - Configure Nagios
After the installation phase is complete, you can find the default configuration of Nagios in /usr/local/nagios/.
We will configure Nagios and Nagios contact.
Edit default nagios configuration with vim:
vim /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
uncomment line 51 for the host monitor configuration.
cfg_dir=/usr/local/nagios/etc/servers
Save and exit.
Add a new folder named servers:
mkdir -p /usr/local/nagios/etc/servers
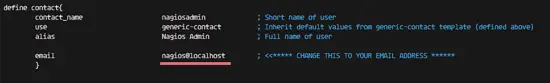
The Nagios contact can be configured in the contact.cfg file. To open it use:Then replace the default email with your own email.
vim /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/contacts.cfg
Configuring Apache
Step 1 - enable Apache modules
You can use the htpasswd command to configure a user nagiosadmin for the nagios web interfacesudo a2enmod rewritesudo a2enmod cgi
sudo htpasswd -c /usr/local/nagios/etc/htpasswd.users nagiosadmin
and type your password.Step 2 - enable the Nagios virtualhost
sudo ln -s /etc/apache2/sites-available/nagios.conf /etc/apache2/sites-enabled/
Step 3 - Start Apache and Nagios
service apache2 restartservice nagios start
Starting nagios (via systemctl): nagios.serviceFailed
cd /etc/init.d/cp /etc/init.d/skeleton /etc/init.d/nagios
vim /etc/init.d/nagios
DESC="Nagios"NAME=nagiosDAEMON=/usr/local/nagios/bin/$NAMEDAEMON_ARGS="-d /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg"PIDFILE=/usr/local/nagios/var/$NAME.lock
chmod +x /etc/init.d/nagiosservice apache2 restartservuce nagios start
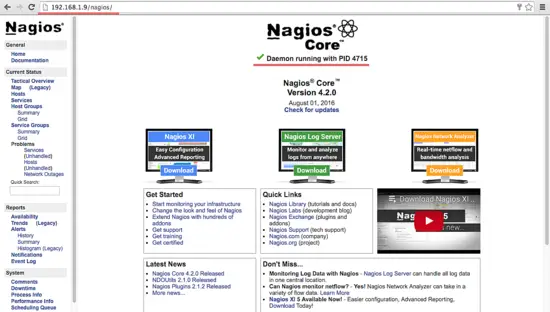
Testing the Nagios Server
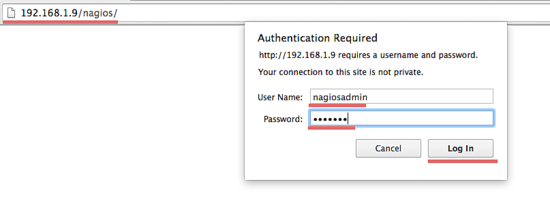
Please open your browser and access the Nagios server ip, in my case: http://192.168.1.9/nagios.Nagios Login with apache htpasswd.
Nagios Admin Dashboard
Adding a Host to Monitor
In this tutorial, I will add an Ubuntu host to monitor to the Nagios server we have made above.Nagios Server IP : 192.168.1.9
Ubuntu Host IP : 192.168.1.10Step 1 - Connect to ubuntu host
ssh root@192.168.1.10
Step 2 - Install NRPE Service
sudo apt-get install nagios-nrpe-server nagios-plugins
Step 3 - Configure NRPE
After the installation is complete, edit the nrpe file /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfg:vim /etc/nagios/nrpe.cfgserver_address=192.168.1.9
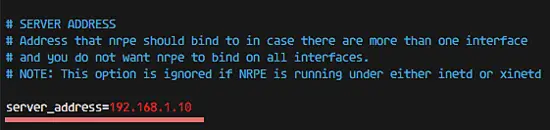
Step 4 - Restart NRPE
service nagios-nrpe-server restart
Step 5 - Add Ubuntu Host to Nagios Server
Please connect to the Nagios server:ssh root@192.168.1.9
vim /usr/local/nagios/etc/servers/ubuntu_host.cfg
Add the following lines:# Ubuntu Host configuration fileYou can find many check_command in /usr/local/nagios/etc/objects/commands.cfg file. See there if you want to add more services like DHCP, POP etc.define host { use linux-server host_name ubuntu_host alias Ubuntu Host address 192.168.1.10 register 1 } define service { host_name ubuntu_host service_description PING check_command check_ping!100.0,20%!500.0,60% max_check_attempts 2 check_interval 2 retry_interval 2 check_period 24x7 check_freshness 1 contact_groups admins notification_interval 2 notification_period 24x7 notifications_enabled 1 register 1 } define service { host_name ubuntu_host service_description Check Users check_command check_local_users!20!50 max_check_attempts 2 check_interval 2 retry_interval 2 check_period 24x7 check_freshness 1 contact_groups admins notification_interval 2 notification_period 24x7 notifications_enabled 1 register 1 } define service { host_name ubuntu_host service_description Local Disk check_command check_local_disk!20%!10%!/ max_check_attempts 2 check_interval 2 retry_interval 2 check_period 24x7 check_freshness 1 contact_groups admins notification_interval 2 notification_period 24x7 notifications_enabled 1 register 1 } define service { host_name ubuntu_host service_description Check SSH check_command check_ssh max_check_attempts 2 check_interval 2 retry_interval 2 check_period 24x7 check_freshness 1 contact_groups admins notification_interval 2 notification_period 24x7 notifications_enabled 1 register 1 } define service { host_name ubuntu_host service_description Total Process check_command check_local_procs!250!400!RSZDT max_check_attempts 2 check_interval 2 retry_interval 2 check_period 24x7 check_freshness 1 contact_groups admins notification_interval 2 notification_period 24x7 notifications_enabled 1 register 1}
And now check the configuration:
/usr/local/nagios/bin/nagios -v /usr/local/nagios/etc/nagios.cfg
... to see if the configuration is correct.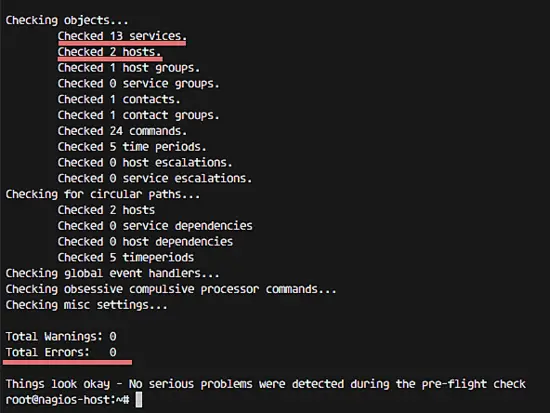
Step 6 - Restart all services
On the Ubuntu Host start NRPE Service:
service nagios-nrpe-server restart
... and on the Nagios server, start Apache and Nagios:service apache2 restartservice nagios restart
Step 7 - Testing the Ubuntu Host
Open the Nagios server from the browser and see the ubuntu_host being monitored.The Ubuntu host is available on monitored host.
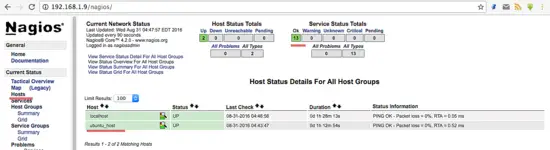
All services monitored without error.
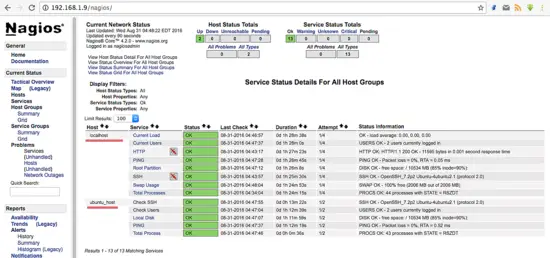
Comments
Post a Comment